Diagnosis Of Posterior Cortical Atrophy
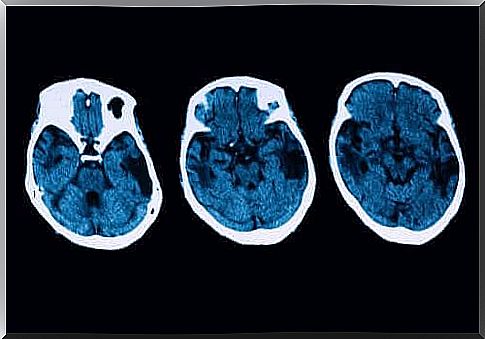
Posterior cortical atrophy is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects a person’s vision. People lose all or part of their sight. Memory loss is also a common symptom. In today’s article, we’ll take a look at this condition and show you how to diagnose it in a timely manner.
Some research indicates that this condition is often not diagnosed early enough. The reason is because it causes visual symptoms, and people often see an ophthalmologist instead of a neurologist.
The phases of posterior cortical atrophy

Medical studies reveal a series of stages of posterior cortical atrophy. Ideally, these symptoms should be discussed with a neurologist as soon as possible in order to start treatment right away.
- Gradual vision problems: A person may see shadows or sometimes lose their vision altogether. Vision failure is so progressive and slow that it doesn’t attract attention until it gets much worse.
- Absence of an ophthalmic clinical picture: When a person goes to an ophthalmologist, that doctor cannot identify the condition leading to the loss of vision. Therefore, the person suffering from it will continue to lead a normal life until the symptoms worsen.
- Minor amnesia: As the condition worsens, there will be a minor amnesia that some consider normal. As the disease progresses, these memory problems will worsen.
- Onset of dementia: A person with this condition will exhibit hypometabolism and hypoperfusion, which can be detected thanks to a test that uses a neuroimaging study. Remember, however, that dementia develops when the disease is fairly advanced.
Diagnosis
As you can see, the symptoms of posterior cortical atrophy are very slowly but steadily progressive. Therefore, by the time a person sees a neurologist, it may already be too late.
So if you notice that your vision is deteriorating, coupled with a slight loss of memory, do not hesitate to see a specialist.
The first test to diagnose posterior cortical atrophy is a blood test. This test allows a specialist to detect vitamin deficiencies, among other findings. After that, a doctor will perform a complete ophthalmic examination.
Diagnostic tests don’t stop there, though. To clear up any doubts, there will be other neurological tests, such as MRIs and tomographs. If everything indicates that you may have posterior cortical atrophy, there are several treatments to choose from.
Treatment of posterior cortical atrophy

If you are diagnosed with this condition, there are two possible treatments you can follow. It is important to know that none of these treatments can cure the disease. So it is a degenerative disease.
Initial treatment involves the use of medications to treat symptoms that may occur as a result of this condition. The drugs reduce anxiety and improve any existing depression.
A patient may also undergo cognitive therapy to preserve the unaffected skills and delay their loss. Patients may also receive physical therapy, something that can help improve these conditions.
These two treatment options mainly focus on improving a person’s quality of life and only treat their symptoms. The goal here is to delay the deterioration of their skills and their ability. This can help relieve the anxiety and depression that can accompany this illness.
When in doubt, talk to a doctor
We want to make you aware of the symptoms of posterior cortical atrophy through this article. This allows you to recognize the first symptoms and consult your doctor as soon as possible. As mentioned earlier, early diagnosis will make a big difference. Don’t worry, help is available.